Purpose
This study aimed to examine the effect of add-on treatment with the neurosteroid pregnenolone (PREG) on neurocognitive dysfunctions of patients with recent-onset schizophrenia (SZ) and schizoaffective disorder (SA).
Method
Sixty out- and inpatients that met DSM-IV criteria for SZ/SA were randomized to an 8-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, 2-center trial. Participants received either pregnenolone (50 mg/d) or placebo added on to antipsychotic medications. Computerized Cambridge Automated Neuropsychological Test Battery measures were administered at baseline and after 4 and 8 weeks of treatment. ANOVA and paired t- or z-tests were applied to examine between- and within-group differences over time.
Results
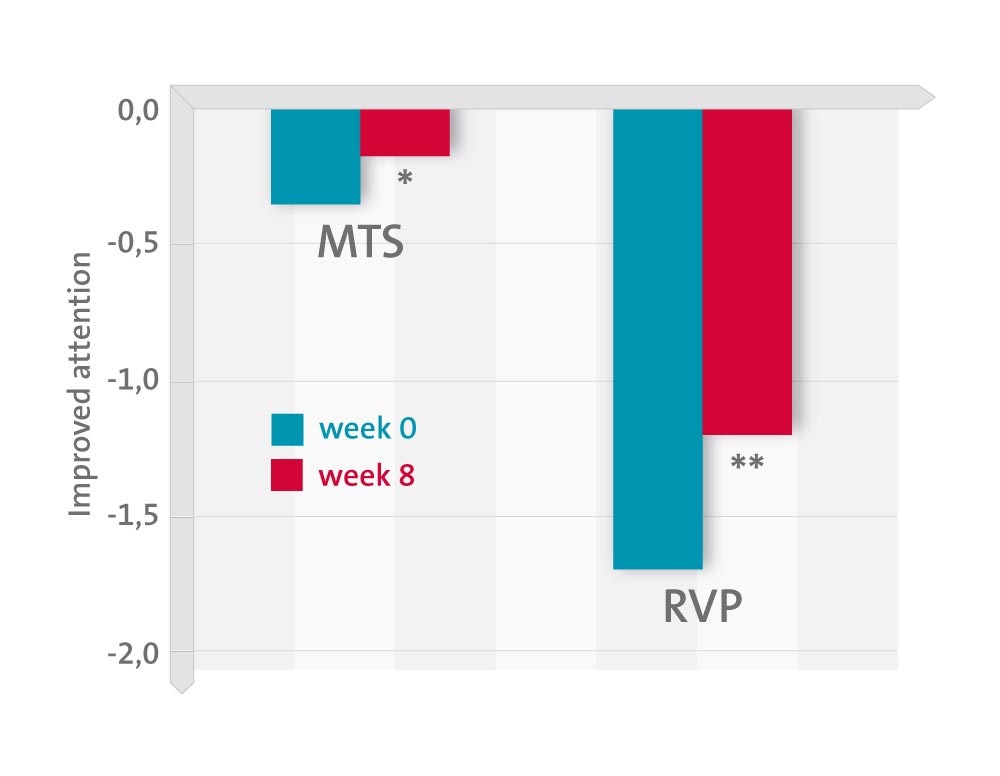
Compared to placebo, adjunctive PREG significantly reduced the deficits in visual attention measured with the Matching to Sample Visual Search task (p=0.002), with moderate effect sizes (d=0.42). In addition, a significant improvement was observed from baseline to end-of-study with respect to the visual (p=0.008) and sustained attention (Rapid Visual Information Processing, p=0.038) deficits, and executive functions (Stockings of Cambridge, p=0.049; Spatial Working Memory, p<0.001) among patients receiving PREG but not among those receiving placebo (all p’s>0.05). This beneficial effect of PREG was independent of the type of antipsychotic agents, gender, age, education, and illness duration.
Conclusions
Pregnenolone augmentation demonstrated significant amelioration of the visual attention deficit in recent-onset SZ/SA. Long-term, large-scale studies are required to obtain greater statistical significance and more confident clinical generalization.